Tools
Smarter Tool Creation with 3D Printing and High-Performance Filaments
In today’s fast-paced industrial environment, innovation is key to staying ahead. One area seeing massive innovation is tool production—thanks to 3D printing. Combined with advanced 3D printer filaments, additive manufacturing is enabling the fast, cost-effective creation of custom tools, jigs, fixtures, and functional components across industries.
Whether it’s for assembly, maintenance, calibration, or testing, tools are essential on the shop floor. With 3D printing, manufacturers and engineers can create highly customized tools with greater flexibility than ever before—without the time and expense of traditional machining.
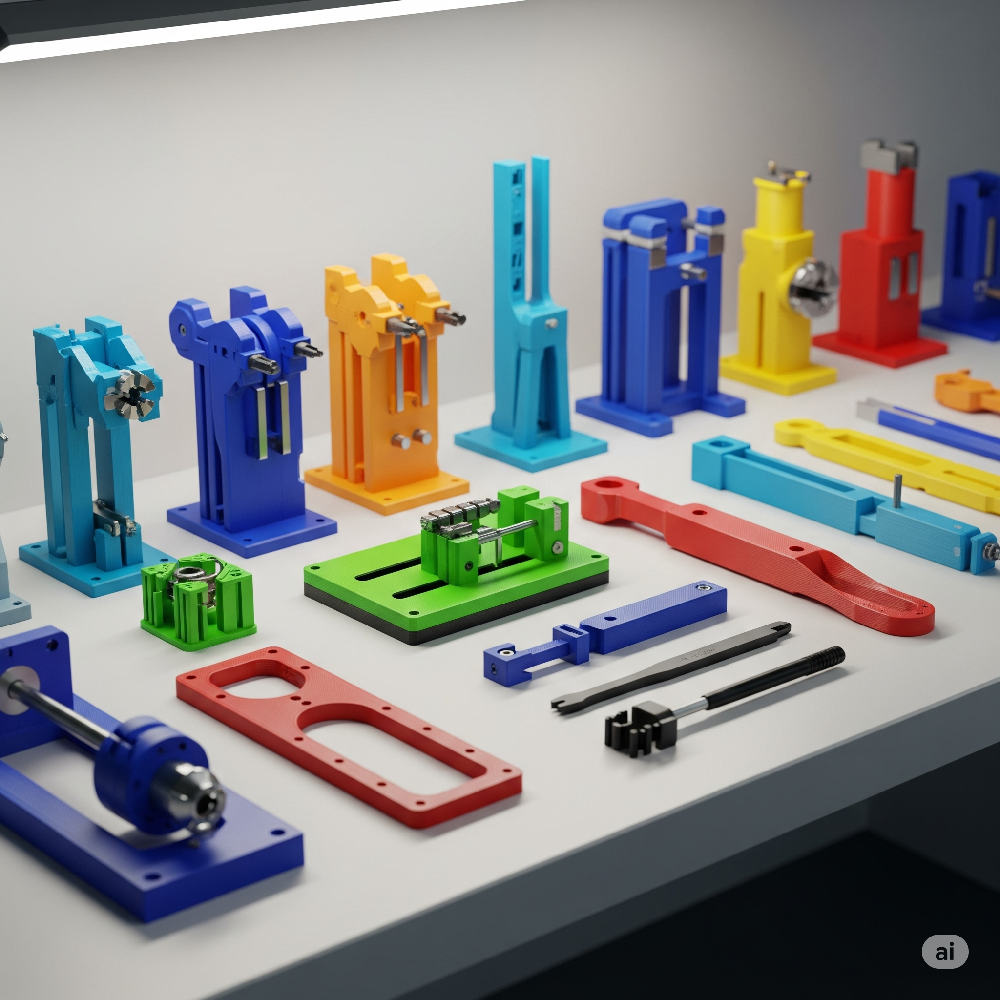
1. How 3D Printing is Used to Make Tools
3D printed tools are increasingly used in a wide range of industrial and mechanical applications. Their flexibility, ease of iteration, and ability to be tailored for specific tasks make them ideal for:
- Custom Jigs and Fixtures: Enhance production accuracy and efficiency with part-specific fixtures.
- Assembly Tools:Lightweight, ergonomic tools designed to improve safety and reduce strain.
- Inspection and Measurement Tools:Custom gauges, holders, or alignment devices for quality control.
- Maintenance Tools:Replacement or specialized tools created on-demand for unique or legacy equipment.
- Functional Hand Tools:Durable, usable implements like wrenches, handles, and holders designed with high-performance 3D printing filaments.
With additive manufacturing, companies are no longer limited to off-the-shelf solutions—they can print the exact tool they need, when they need it.
2. Best 3D Printer Filaments for Tool Production
The performance of your 3D printed tool depends heavily on the 3D printer filament you use. For tools, strength, durability, heat resistance, and wear tolerance are crucial.
Top filaments for tool-making include:
- Nylon (PA):Known for toughness and wear resistance, perfect for mechanical and load-bearing tools.
- Polycarbonate (PC): High impact strength and temperature resistance—ideal for functional tools under stress.
- ABS: Great all-around industrial filament for strong, lightweight, and impact-resistant tools.
- Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Filaments: These filaments combine lightweight properties with high stiffness and reduced flex, ideal for jigs and structural tools.
- PETG: Offers excellent chemical resistance and ease of printing for general shop tools and brackets.
- TPU (Flexible Filament): Useful for grips, bumpers, or protective components within tool systems.
Choosing the right 3D filament for tools ensures you’re building components that can withstand industrial conditions without failure.
3. Benefits of 3D Printed Tools
- Speed: Design and print tools in-house in a matter of hours—no need to wait for outside suppliers.
- Customization: Tools tailored to the specific geometry of your parts or machinery.
- Cost Savings:Cut down on machining and mold costs, especially for low-volume or one-off items.
- Weight Reduction: Create lightweight tools that reduce operator fatigue without compromising strength.
- On-Demand Production:Replace lost or damaged tools quickly to minimize downtime.
These advantages make 3D printed tools a practical and strategic choice for workshops, manufacturing lines, and maintenance teams.
4. Real-World Applications
- Automotive:Custom wheel alignment tools, ergonomic handles, and torque aids.
- Aerospace:Lightweight composite layup tooling and specialty assembly jigs.
- Electronics: ESD-safe tools printed with conductive or anti-static filaments for sensitive environments.
- Maintenance Crews: Printed spanners, holders, and enclosures customized for specific equipment.
Companies are increasingly turning to 3D printer filament solutions to produce fast, functional tools that enhance productivity and safety.


5. The Future of 3D Printed Tools
As 3D printing technology and filaments continue to improve, expect even greater integration into everyday tooling operations. High-temperature filaments, metal-filled composites, and specialized engineering materials are expanding what’s possible, enabling stronger, more durable, and even multi-material tools.
The future is a hybrid of digital design, additive manufacturing, and smart material selection—and tools are just the beginning.
Conclusion: Better Tools Start with Better Filament
The age of waiting weeks for custom tools or paying a premium for specialized fixtures is over. With the right 3D printer filament, you can build better tools in-house—faster, cheaper, and perfectly tailored to your needs. Explore our collection of high-performance 3D printer filaments and discover how you can start creating better tools today.


