Mold & Tooling
Revolutionizing Molding and Tooling with 3D Printing and Filament Technology
In the world of manufacturing, efficiency and precision are everything. Traditionally, molding and tooling have relied on expensive, time-consuming methods like CNC machining and metal casting. But with the rise of 3D printing, the landscape is changing—and at the center of this shift is the evolution of 3D printer filament technology.
Today, manufacturers and engineers are using 3D printed molds and tools not just for prototyping, but also for low- to medium-volume production. Whether you’re in injection molding, thermoforming, or composite layup, the right 3D printing setup combined with the right filament can dramatically cut lead times and costs.
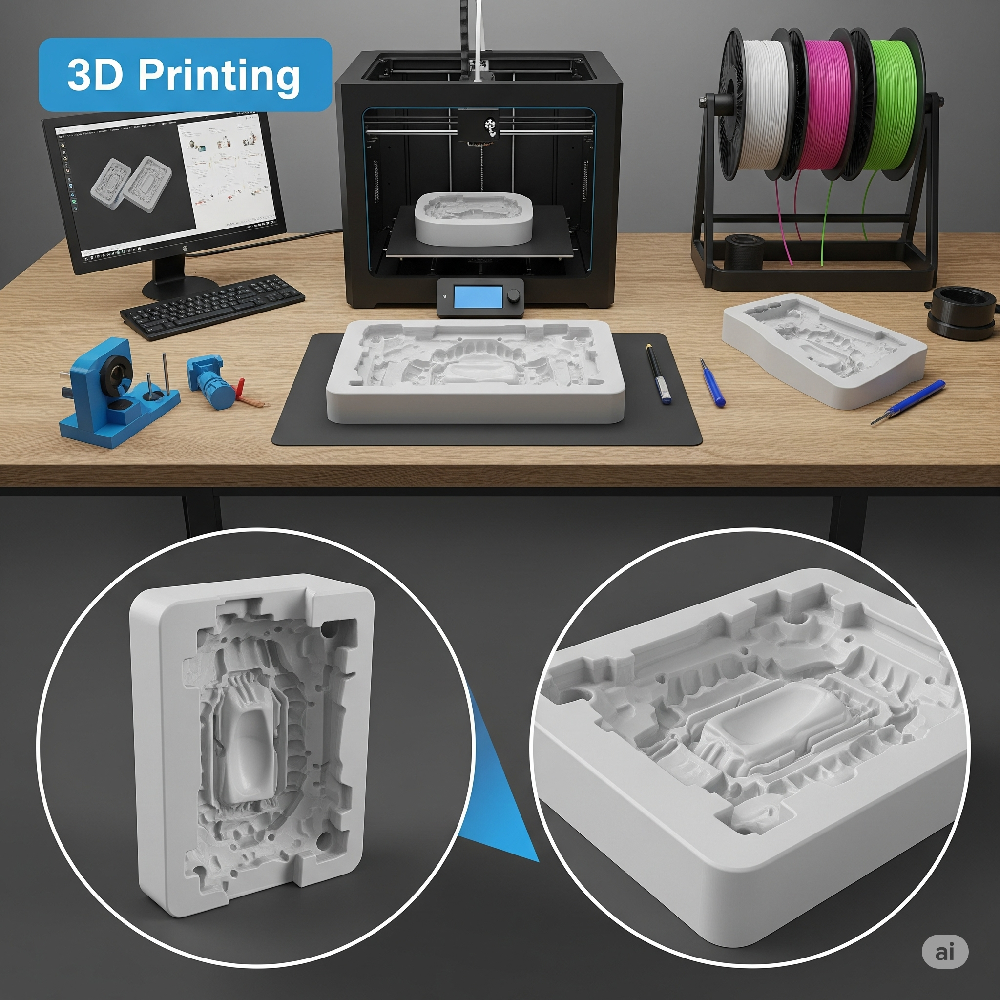
1. How 3D Printing is Used in Molding and Tooling
3D printing enables rapid creation of custom molds, jigs, fixtures, and tooling components. Engineers can go from CAD to functional tool in a matter of hours, allowing for faster iterations and shorter product development cycles.
Key applications include:
- Injection Molding Molds: For small-batch runs, 3D printed molds offer an affordable alternative to metal.
- Thermoforming Tools: Custom vacuum form molds can be printed using heat-resistant 3D printer filaments.
- Composite Layup Tools: Aerospace and automotive industries use 3D printed forms to lay up carbon fiber and other composites.
- Jigs and Fixtures: Improve assembly line productivity with custom-fit tools and alignment aids.
2. Choosing the Right 3D Printer Filament for Tooling
Selecting the proper 3D filament is crucial for successful tooling. The demands on printed tools—heat resistance, strength, wear tolerance—require more than standard PLA.
Commonly used filaments for tooling applications include:
- Nylon (PA): Highly durable and abrasion-resistant; ideal for mechanical parts and jigs.
- Polycarbonate (PC): High heat resistance and strength; great for forming and mold tooling.
- ABS: A popular choice due to its balance of toughness and heat resistance.
- Carbon Fiber-Filled Filaments: Reinforced for superior stiffness and reduced warping; perfect for functional end-use tooling.
- PETG: Offers chemical resistance and good mechanical properties for general-purpose fixtures.
Using engineering-grade 3D printer filaments ensures that your printed molds and tools can stand up to the demands of the shop floor.
3. Benefits of 3D Printed Molding and Tooling
- Reduced Lead Times: Traditional metal tooling can take weeks; 3D printing can deliver in hours or days.
- Cost Savings: Eliminates the need for expensive CNC machining or casting for early-stage development.
- Rapid Iteration: Easy to modify and reprint molds or fixtures as designs evolve.
- Customization: Create bespoke tooling tailored to unique parts or assembly needs.
- Lightweighting: 3D printed tools can be designed for strength without unnecessary mass, reducing strain on workers and machines.
4. Real-World Examples
- Consumer Goods: Brands use 3D printed molds to prototype packaging before committing to mass production.
- Automotive: Custom jigs and fixtures are printed in-house to speed up part inspections and assembly.
- Aerospace: Complex composite layup molds are produced with high-performance filaments to reduce lead times and costs.
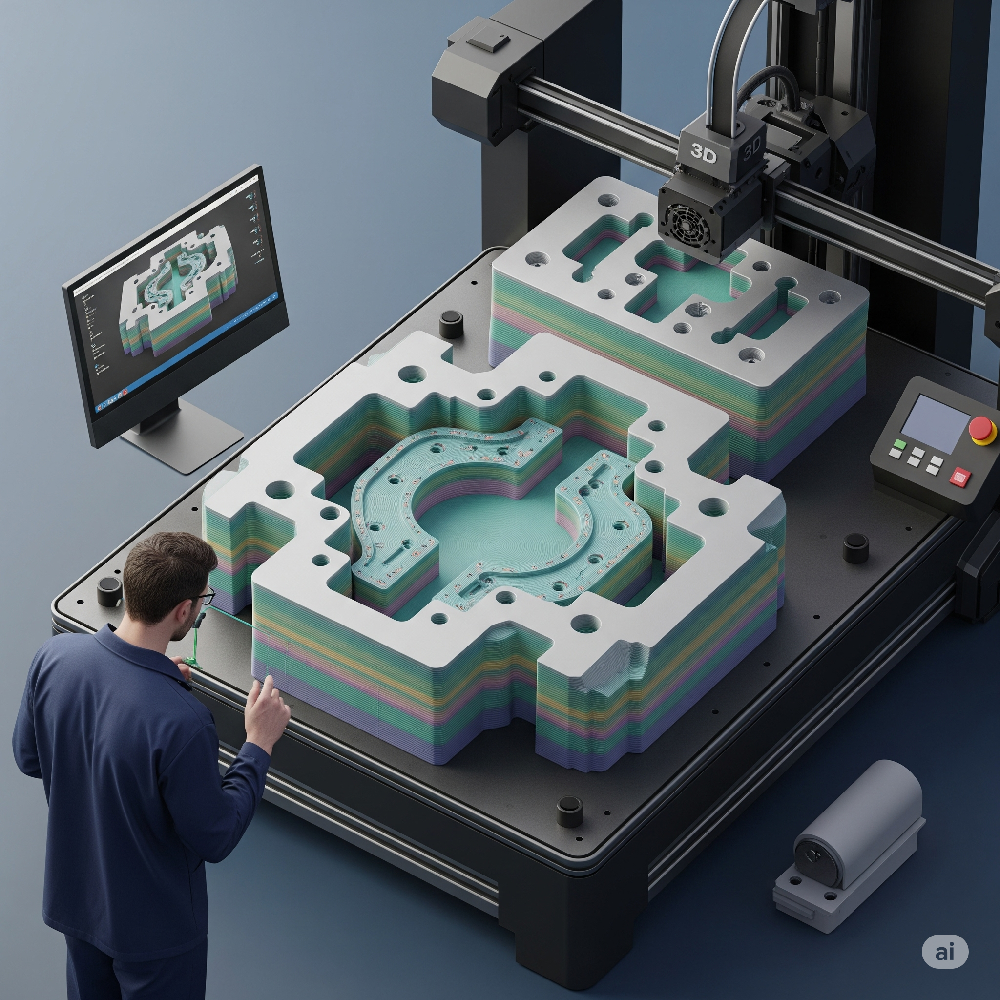

5. Looking Ahead: The Future of Tooling with 3D Printing
As 3D printer filaments continue to evolve, so does the potential for tooling. New formulations offer increased thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance. Materials like PEI (Ultem), PPSU, and even metal-infused filaments are expanding the boundaries of what’s possible in additive manufacturing.
Conclusion: The Smart Choice for Modern Tooling
The integration of 3D printing in molding and tooling isn’t just a trend—it’s a smarter, faster, and more economical way to work. With the right 3D printer filament, manufacturers can unlock greater design flexibility, improve production workflows, and stay ahead of the competition. Ready to upgrade your tooling process? [Explore our selection of industrial-grade 3D printer filaments now.]


