Education
Empowering Learning: How 3D Printing and Filaments Are Revolutionizing Education
In classrooms around the world, hands-on learning is more important than ever. 3D printing has emerged as a transformative educational tool, allowing students and educators to bring abstract concepts to life. At the heart of this innovation lies the versatility of 3D printer filament, which makes it possible to print everything from molecular models to functional robotics parts. Here’s how 3D printing and advanced filaments are reshaping education at every level.

1. Bringing STEM Concepts to Life
Traditional lectures and textbooks can only do so much to illustrate complex ideas. With 3D printed models:
- Science: teachers can print anatomical structures, geological formations, or molecular bonds, helping students visualize otherwise intangible subjects.
- Technology:courses can use printed casings and components to teach circuitry, sensors, and mechatronics.
- Engineering:students prototype bridges, load-bearing beams, and mechanical linkages to test stress, strain, and geometry in real time.
- Mathematics:classes benefit from tangible geometric shapes—polyhedra, conic sections, and fractal forms—that aid spatial reasoning.
By leveraging the right 3D printer filaments—such as PLA for simple models, PETG for functional parts, or even magnetic filaments for interactive demos—educators can turn abstract theory into engaging, hands-on lessons.
2. Fostering Creativity and Design Thinking
3D printing encourages students to move from passive consumers of information to active designers:
- Project-Based Learning:Students identify problems, brainstorm solutions, and iterate prototypes using CAD software and 3D printing filament.
- Art & Design: From sculptural pieces to jewelry and fashion accessories, creative classes can experiment with textures and finishes using specialty filaments like wood- or metal-filled PLA.
- Architecture:Print scale models of buildings, neighborhoods, and city layouts to explore urban planning and aesthetics.
This cycle of design, print, test, and refine teaches critical thinking, problem-solving, and resilience—essential skills for the 21st-century workforce.
3. Accessible, Low-Cost Prototyping
Gone are the days when prototyping required expensive mold tooling or bulk machining:
- Budget-Friendly Filaments: PLA and PETG offer excellent print quality at low cost, making them ideal for classroom budgets.
- On-Demand Fabrication:Need a custom lab fixture or replacement part? Teachers and students can print it overnight, avoiding delays and expensive orders.
- Safety and Ease: Filaments like PLA are biodegradable and emit minimal odors, making them suitable for indoor school environments.
This democratization of fabrication empowers every student to experiment without worrying about material waste or prohibitive expenses.
4. Building Career-Ready Skills
Exposure to additive manufacturing and filament selection prepares students for future careers:
- Industry Standards: Working with engineering-grade filaments such as ABS, Nylon, and Carbon Fiber–reinforced materials teaches real-world material properties.
- CAD Proficiency: Mastery of 3D modeling tools and slicing software is directly transferable to engineering, architecture, and product design roles.
- Rapid Iteration Mindset: Iterative design and testing with 3D printer filaments instill agile development practices valued in tech and manufacturing sectors.
By integrating 3D printing into curricula, schools help bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and hands-on technical expertise.
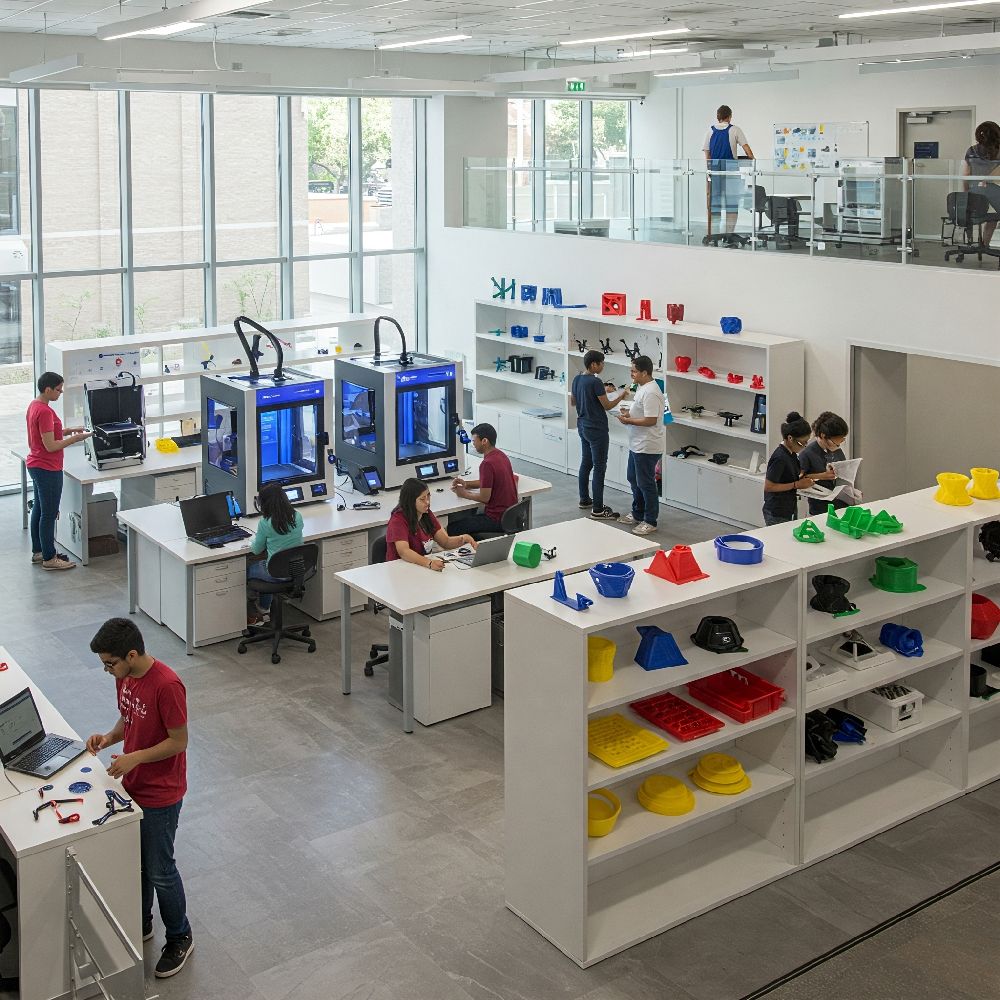

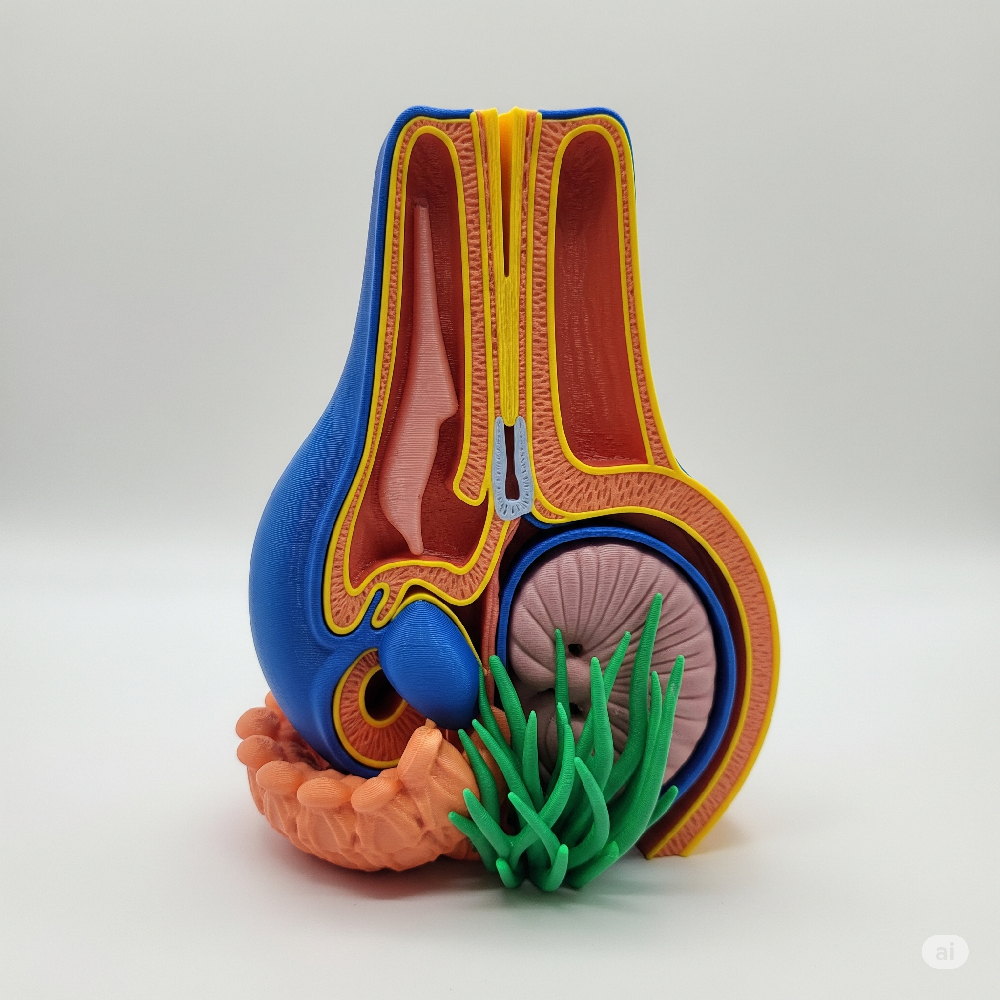
5. Real-World Educational Success Stories
- University Maker Spaces: Engineering departments print drone components, prosthetic prototypes, and research apparatus with specialty filaments.
- K-12 STEM Clubs:Middle and high school teams build robots, contest entries, and scientific models, often winning regional competitions thanks to rapid prototyping.
- Vocational Training:Technical schools teach automotive, aerospace, and dental students to print jigs, dental molds, and replacement parts using high-temperature, certified filaments.
These examples highlight how 3D printing and filament technology can scale from primary classrooms to advanced research labs.
6. The Future of 3D Printing in Education
As 3D printer filaments evolve, educational possibilities expand:
- Multi-Material Printing:Combine rigid and flexible filaments in one print for lifelike anatomical models or soft-touch grips.
- Conductive and Smart Filaments: Integrate electronics directly into printed objects, enabling wearable devices or interactive sculptures.
- Sustainable Materials: Bio-based, recycled, and compostable filaments support environmental science projects and teach eco-responsibility.
By staying at the forefront of filament innovation, schools can continually refresh curricula and keep students engaged with cutting-edge technology
Conclusion: Print the Future of Learning
From igniting curiosity to building practical skills, 3D printing and the right filaments are redefining education. Whether you’re an educator looking to enrich your STEM program or a school administrator planning a makerspace, now is the time to harness additive manufacturing for deeper learning and innovation. Explore our selection of education-friendly 3D printer filaments—from low-cost PLA to advanced engineering materials—and empower the next generation of makers and thinkers.


